In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of Express js routing, how to define and handle different HTTP methods, and use route parameters and middleware to build powerful web APIs. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to brush up your knowledge, this article will walk you through the essentials with examples.
Table of Contents
Express.js is one of the most popular web application frameworks for Node.js. It provides a minimal and flexible set of features for building web and mobile applications. At the heart of Express.js lies its routing capabilities, which allow developers to handle HTTP requests efficiently.
By the end, you’ll understand how to structure routes effectively in your Express.js applications.
1. What is Express js Routing?
Express js Routing refers to defining your application’s endpoints and how it should respond to client requests. Each route can react to a different HTTP method, like GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE.
With Express js routing, you can create a clear structure for how your server handles incoming requests — whether you’re building a simple website or a full-fledged REST API.
Express js Routing refers to defining how an application responds to client requests at a particular URL (endpoint). Each route consists of:
- An HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- A path (URI)
- A handler function (callback that executes when the route is matched)
Basic Syntax
app.METHOD(PATH, HANDLER)
- app → Express instance
- METHOD → HTTP method (e.g., app.get(), app.post())
- PATH → URL path (e.g., /users, /posts)
- HANDLER → Function that processes the request
Installing Express.js
Before diving into Express js routing, let’s set up Express in a Node.js project.
Step 1: Initialize a Node.js project
mkdir express-routing-demo cd express-routing-demo npm init -y
Step 2: Install Express.js
npm install express
Step 3: Create a basic server
Create a file named server.js:
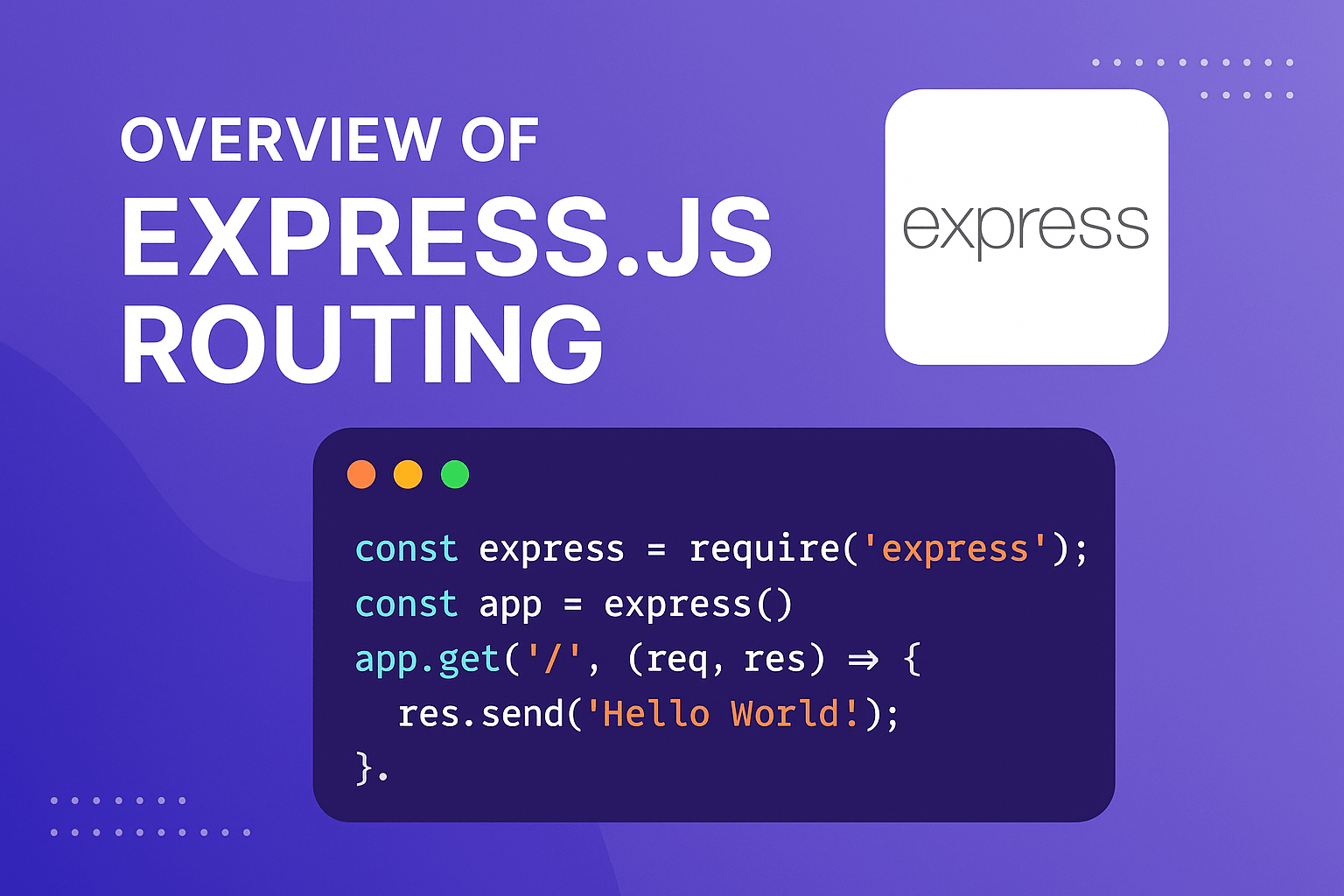
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
Now you’re ready to start building routes!
Basic Express js Routing
A route in Express consists of:
-
A path (URL)
-
An HTTP method
-
A callback function (called when the route is matched)
Example: Simple GET route
Example: POST request handler
Example: PUT and DELETE
These examples cover basic Express js routing for each HTTP method.
Route Parameters
Route parameters allow you to capture values embedded in the URL.
Example:
If you navigate to /user/42The server will respond with User ID is 42.
You can use multiple parameters:
Query Parameters
Query parameters come after the ? in a URL and are useful for filtering and searching.
Example:
Request: GET /search?q=express
Response: Search results for: express
Express Router: Modular Routing
For larger applications, it’s a good practice to separate routes into different modules using express.Router().
Example: userRoutes.js
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();router.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('List of users');
});
router.get('/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send(`User ID: ${req.params.id}`);
});
module.exports = router;
In main server.js
Now /users and /users/:id will be handled by the userRoutes file.
Middleware in Routes
Middleware functions can be used before route handlers to perform tasks like authentication or logging.
Example:
const logger = (req, res, next) => {
console.log(`Request URL: ${req.url}`);
next();
};app.get('/dashboard', logger, (req, res) => {
res.send('Dashboard');
});
Handling 404 Errors
To catch undefined routes, add a 404 handler at the end:
RESTful Express.js Routing
Express is commonly used to build RESTful APIs. Here’s a pattern you might follow:
Example:
app.get('/products', (req, res) => {
res.send('Get all products');
});
app.get('/products/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Get product with ID ${req.params.id}`);
});
app.post('/products', (req, res) => {
res.send('Create new product');
});
app.put('/products/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Update product ${req.params.id}`);
});
app.delete('/products/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Delete product ${req.params.id}`);
});
Best Practices for Express JS Routing
-
Use express.Router() for modular code.
-
Validate route parameters to avoid errors.
-
Add middleware for reusability (e.g., authentication, logging).
-
Keep routes RESTful and consistent.
-
Group similar routes together for better organization.
References
Credits:
Conclusion
Express js Routing is a fundamental part of building Express.js applications. With its simple syntax and powerful capabilities, Express lets you handle HTTP requests efficiently using different HTTP methods, parameters, and middleware. Whether you’re developing a simple web server or a robust REST API, mastering Express routing is key.
By organizing routes modularly and following best practices, you can build scalable and maintainable Node.js applications with ease.
